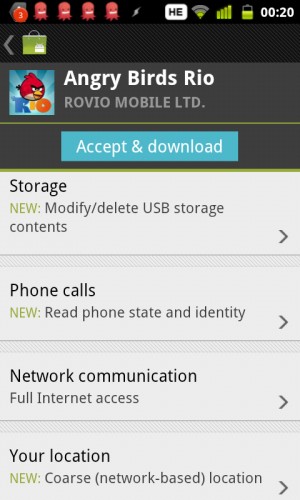
The binary choice has left most users ignoring permission warnings and sacrificing personal data. Most applications aggressively eavesdrop on their users, from monitoring their online habits through the device identifier to tracking their movements in the real world via location information.
Now, a research group at North Carolina State University hopes to give the average user a third option. Dubbed NativeWrap, the technology allows Web pages to be wrapped in code and make them appear as a mobile application, but with user-controlled privacy. Because many applications just add a user interface around a Web application, the user should have equivalent functionality for many wrapped apps, said William Enck, assistant professor in the department of computer science at North Carolina State University.
Read 7 remaining paragraphs | Comments