Enlarge (credit: Aviram et al.)
More than 13 million websites and e-mail services protected by the transport layer security protocol are vulnerable to a newly discovered, low-cost attack that decrypts sensitive communications in a matter of hours and in some cases almost immediately, an international team of researchers warned Tuesday. More than 97,000 of the top 1 million most popular Web properties are among the vulnerable HTTPS-protected sites.
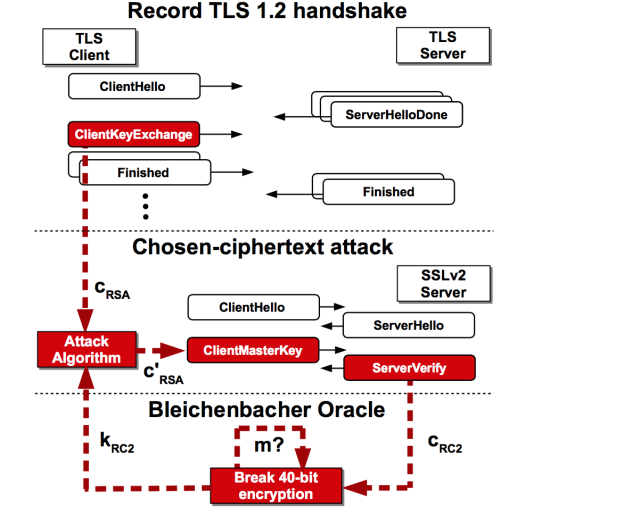
The attack works against TLS-protected communications that rely on the RSA cryptosystem when the key is exposed even indirectly through SSLv2, a TLS precursor that was retired almost two decades ago because of crippling weaknesses. The vulnerability allows an attacker to decrypt an intercepted TLS connection by repeatedly using SSLv2 to make connections to a server. In the process, the attacker learns a few bits of information about the encryption key each time. While many security experts believed the removal of SSLv2 support from browser and e-mail clients prevented abuse of the legacy protocol, some misconfigured TLS implementations still tacitly support the legacy protocol when an end-user computer specifically requests its use. The most notable implementation subject to such fatal misconfigurations is the OpenSSL cryptographic library, which on Tuesday is expected to release an update that makes such settings much less likely to occur.
Recent scans of the Internet at large show that more than 5.9 million Web servers, comprising 17 percent of all HTTPS-protected machines, directly support SSLv2. The same scans reveal that at least 936,000 TLS-protected e-mail servers also support the insecure protocol. That's a troubling finding, given widely repeated advice that SSLv2—short for secure sockets layer version 2—be disabled. More troubling still, even when a server doesn't allow SSLv2 connections, it may still be susceptible to attack if the underlying RSA key pair is reused on a separate server that does support the old protocol. A website, for instance, that forbids SSLv2 may still be vulnerable if its key is used on an e-mail server that allows SSLv2. By the researchers' estimate, that leaves 13.6 million HTTPS-protected websites and a significant number of TLS-protected e-mail servers open to attack.