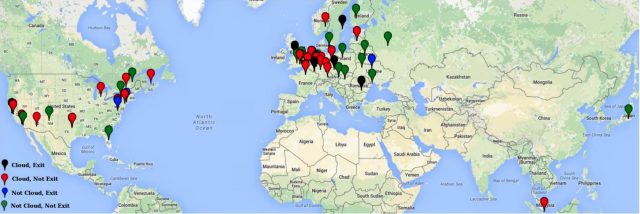
Enlarge / A map of hidden services directories detected as malicious.
The trust of the Tor anonymity network is in many cases only as strong as the individual volunteers whose computers form its building blocks. On Friday, researchers said they found at least 110 such machines actively snooping on Dark Web sites that use Tor to mask their operators' identities.
All of the 110 malicious relays were designated as hidden services directories, which store information that end users need to reach the ".onion" addresses that rely on Tor for anonymity. Over a 72-day period that started on February 12, computer scientists at Northeastern University tracked the rogue machines using honeypot .onion addresses they dubbed "honions." The honions operated like normal hidden services, but their addresses were kept confidential. By tracking the traffic sent to the honions, the researchers were able to identify directories that were behaving in a manner that's well outside of Tor rules.
"Such snooping allows [the malicious directories] to index the hidden services, also visit them, and attack them," Guevara Noubir, a professor in Northeastern University's College of Computer and Information Science, wrote in an e-mail. "Some of them tried to attack the hidden services (websites using hidden services) through a variety of means including SQL Injection, Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), user enumeration, server load/performance, etc."